
Understanding micron to gauge stretch film conversion is essential for selecting the correct stretch film to meet packaging needs. Micron to gauge stretch film measures thickness, while other stretch film like bundling stretch film applies this for securing smaller loads. Both micron and gauge serve as key metrics, helping to determine the thickness and performance of the film. These measurements directly impact the film’s ability to protect goods during transit or storage. A higher gauge or micron value means thicker film, which typically offers better puncture resistance and durability. Micron to gauge stretch film refers to thickness measured in microns (the modern metric standard) or gauges, ensuring the right film thickness for various products.
Stretch films are widely used in industries such as shipping, packaging, and storage, where secure pallet wrapping is essential for palletizing goods, bundling products, and preventing damage. Selecting the appropriate film thickness ensures the packaging process is efficient and cost-effective, as well as providing adequate protection. Conversions between micron and gauge enable businesses to select the right stretch film thickness for specific applications.
Why Choose Our Stretch Film Over Competitors?

| Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Place of Origin | Fujian, China |
| Brand Name | PWP Stretch Film |
| Product Name | Micron to Gauge Stretch Film |
| Material | LDPE + LLDPE |
| Size | Customized |
| Thickness | Customized |
| Length | Customized |
| Width | Customized |
| Color | Customized |
| Features | Moisture-proof |
| Hardness | Soft |
| Logo | Accept customized logo printing |
| Processing Type | Casting, Multiple Extrusion |
| Transparency | Transparent, Translucent, Opaque |
| Tensile Strength | 150.0-200.0 MPa |
| Certificate | SGS, ISO, MSDS |
| Advantages | Factory Direct Sales |
| Service | OEM |
| Type | Hand/Machine/Jumbo Roll |
| Packing | Carton |
| Minimum Order Quantity | 2 kg |
Micron to gauge stretch film refers to the thickness of stretch film measured in two common units: microns and gauge. Gauge is a traditional unit of measurement used in the packaging industry, primarily in the U.S., to quantify the thickness of films. A higher gauge value indicates a thicker film, which generally correlates with enhanced durability, puncture resistance, and load containment. On the other hand, the micron, a metric measurement, allows for more precise calculations and is often used globally.
Gauge is a measurement standard commonly used for thin plastics like stretch film or thin plastic rolls. Stretch wrap is typically available in gauges ranging from 37 to 150.
Micron is the new metric standard used for measuring stretch film thickness. It is similar to gauge in that the higher the micron count, the thicker the plastic.
For example, a 60-gauge stretch film is thinner and offers more flexibility, while a 120-gauge film provides better strength and is suited for heavier loads. Understanding how these measurements relate helps businesses choose the appropriate film thickness for different applications. Stretch films with higher gauge values are typically used for heavy-duty packaging, while lower gauge films are ideal for lighter loads or less demanding conditions.
| Gauge | Best Use Case | Strength & Durability | Puncture Resistance | Stretchability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 Gauge Stretch Wrap | Light to medium loads; bundling smaller items | Moderate – suited for fragile goods | Lower resistance to punctures | High flexibility for easy wrapping |
| 80 Gauge Stretch Wrap | Heavy loads up to 2,400 lbs; general-purpose use | High – durable and strong | High resistance to tearing | Standard flexibility |
By understanding the relationship between micron to gauge stretch film, businesses can optimize their packaging choices. Whether using 60 or 80 gauge film, selecting the correct thickness ensures proper load containment, reduced wastage, and improved packaging efficiency.
With these insights into gauge and micron measurements, businesses can confidently choose the right stretch film. Whether the application requires the flexibility of a lighter 60-gauge film or the durability of an 80-gauge wrap, understanding how micron to gauge stretch film works ensures that packaging needs are met efficiently and effectively.
Packaging thickness is crucial because it directly impacts the durability and effectiveness of your packaging. Thin films below specification are prone to cracking, splitting, or leaking, which can compromise the integrity of your product. Additionally, insufficient thickness reduces the barrier properties of the film, allowing oxygen and contaminants to penetrate, leading to faster product degradation. Optimal thickness ensures your packaging is protective and reliable.
Micron to gauge stretch film highlights the need to understand the units used for film thickness. Microns (metric standard) and gauges (traditional unit) are both widely used, and knowing their differences ensures you can select the right thickness for your application. This understanding is critical when working with manufacturers or suppliers who may use different standards.
Knowing how to convert between units like micron to gauge stretch film is essential for accurate communication and decision-making. Conversions allow you to compare specifications, ensure compatibility with equipment, and meet industry requirements. This skill simplifies processes, avoids costly mistakes, and ensures the best packaging for your needs.
In the context of micron to gauge stretch film, the micron serves as a metric measurement used to quantify film thickness with precision. One micron (µm) equals one-thousandth of a millimeter (1 micron = 0.001 mm), making it a highly precise measurement for very thin materials. This level of precision is particularly relevant in industries where the thickness of stretch film plays a critical role in load containment and protection.
Micron measurements allow manufacturers and users to accurately assess the thickness of packaging materials, ensuring that the correct film is chosen for specific tasks. Since small variations in thickness can impact the film’s strength and performance, the micron provides a reliable way to gauge these subtle differences. Stretch film measured in microns offers consistency, which is essential for packaging products with specific containment requirements.
Micron measurements are important for determining the stretch film’s performance characteristics, including its tensile strength, stretchability, and puncture resistance. A higher micron value indicates a thicker and stronger film, ideal for securing heavier loads or protecting goods with sharp edges. Conversely, lower micron films are better suited for lightweight packaging or bundling smaller products where flexibility is more important than strength.
While the gauge system is often used in countries like the U.S., the micron system is widely preferred internationally because it offers a more precise way to define film thickness. In micron to gauge stretch film, understanding the conversion between these units ensures the right film is chosen for the job. For example:
Using both micron and gauge measurements helps businesses standardize their film selection across different regions. The micron measurement ensures precision in manufacturing and packaging operations, while the gauge system provides a practical reference familiar to many industries.
By converting between micron to gauge stretch film, businesses can optimize their film selection based on specific packaging needs. The precision of micron measurements minimizes the risk of using incorrect film thickness, which could lead to product damage during transport. Moreover, knowing how to convert between micron and gauge ensures that global operations and suppliers are aligned in selecting the right film for their applications.
When selecting the right stretch film for packaging needs, understanding the conversion between micron and gauge is essential. This process ensures that the chosen film offers the desired thickness and performance. The formula for converting microns to gauge is straightforward:
Gauge = Micron × 4
This formula highlights that each micron value, when multiplied by four, provides the corresponding gauge value. This simple conversion method enables users to compare films measured in different units easily.
For example:
This method ensures precision in choosing the correct film thickness for specific packaging applications. A higher gauge value corresponds to thicker and more durable film, making it suitable for heavy loads or items with sharp edges. On the other hand, a lower gauge value works well for lighter loads or less demanding packaging needs.

Although the conversion formula is simple, businesses often rely on online micron to gauge stretch film calculators for convenience. These tools allow users to input micron values and receive accurate gauge equivalents instantly. They also support reverse calculations, helping users convert gauge measurements back to microns when needed.
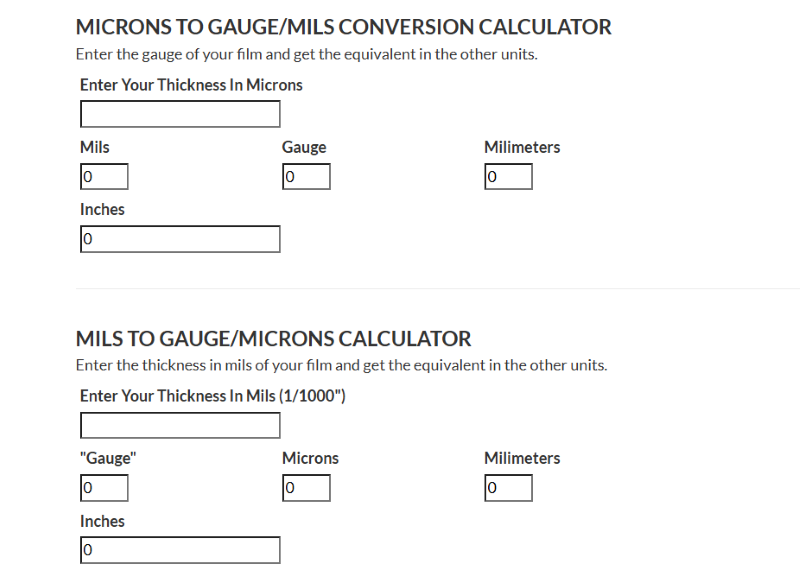
These calculators are especially useful when making bulk orders for stretch films, as precise thickness measurements are crucial for product protection and cost optimization. In industries such as shipping, packaging, and warehousing, ensuring the correct conversion between micron to gauge stretch film prevents the use of inappropriate materials that might compromise load containment.
By mastering the calculation of micron to gauge stretch film, packaging professionals can select the optimal film for any job. The combination of manual conversion formulas and online calculators ensures both accuracy and efficiency, streamlining the film selection process for businesses of all sizes.
A detailed micron to gauge stretch film chart is an essential tool for packaging professionals. It provides quick access to conversions between microns, gauge, and other measurement units such as millimeters (mm) and mil. This chart simplifies the process of selecting the correct stretch film thickness by ensuring accurate conversions across multiple units. The right thickness ensures adequate protection, stability, and containment during transport and storage.
The table below demonstrates some common conversions. A higher gauge or micron value indicates a thicker film, offering better puncture resistance and durability, while a lower value provides more flexibility and stretch.
| Micron (mu) | Gauge (ga) | Mil | Inch (in) | Millimeter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.08 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.0002 | 0.0051 |
| 5.8 | 23 | 0.23 | 0.0002 | 0.0058 |
| 7.6 | 30 | 0.3 | 0.0003 | 0.0076 |
| 10 | 40 | 0.4 | 0.0004 | 0.0101 |
| 12.5 | 50 | 0.5 | 0.0005 | 0.0127 |
| 15 | 60 | 0.6 | 0.0006 | 0.0152 |
| 17.78 | 70 | 0.7 | 0.0007 | 0.0178 |
| 19 | 75 | 0.75 | 0.0007 | 0.019 |
| 20 | 80 | 0.8 | 0.0008 | 0.0203 |
| 23 | 90 | 0.9 | 0.0009 | 0.0228 |
| 25 | 100 | 1 | 0.001 | 0.0254 |
| 30 | 120 | 1.2 | 0.0012 | 0.0304 |
| 38 | 150 | 1.5 | 0.0015 | 0.038 |
| 40 | 160 | 1.6 | 0.0016 | 0.0406 |
| 45 | 180 | 1.8 | 0.0018 | 0.0457 |
| 50 | 200 | 2 | 0.002 | 0.0508 |
| 63.5 | 250 | 2.5 | 0.0025 | 0.0635 |
| 76.2 | 300 | 3 | 0.003 | 0.0762 |
| 88.9 | 350 | 3.5 | 0.0035 | 0.0889 |
| 101.6 | 400 | 4 | 0.004 | 0.1016 |
| 114.3 | 450 | 4.5 | 0.0045 | 0.1143 |
| 127 | 500 | 5 | 0.005 | 0.127 |
| 140 | 550 | 5.5 | 0.0055 | 0.14 |

This micron to gauge stretch film chart helps packaging teams select the correct film based on the required thickness. For example:
Comparing measurements across multiple units ensures consistency when dealing with suppliers or international partners, where some regions might use microns while others use gauge or mil. By understanding these metrics, packaging professionals can confidently select the most appropriate film for their specific needs, avoiding under- or over-packaging issues.
This conversion chart is a practical resource for businesses working with micron to gauge stretch film, helping them align thickness requirements with packaging goals. Whether wrapping fragile products or heavy pallets, this chart ensures that the selected film offers the right balance between strength, stretchability, and protection.
When it comes to selecting the best stretch film for packaging, understanding how different thicknesses work is crucial. Using a micron to gauge stretch film approach ensures precise selection based on load requirements, shipping conditions, and the weight of packaged goods. Choosing the correct gauge impacts both packaging performance and cost-efficiency. Two of the most common stretch film gauges are 80-gauge and 120-gauge. Each has unique strengths, making it ideal for specific use cases.
80-gauge stretch wrap is widely regarded as the industry standard because of its versatility and ability to handle most general-purpose packaging tasks. With a thickness equivalent to 20 microns, it strikes the perfect balance between flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This gauge is well-suited for a wide range of applications, including:
The reason 80-gauge wrap is the standard lies in its ability to maintain strength while offering some stretch. It provides excellent puncture resistance, making it a reliable option for most packaging scenarios. Whether used in warehouses or shipping operations, 80-gauge stretch film ensures that loads remain secure and intact throughout their journey.
Advantages of 80 Gauge Stretch Wrap:
In situations where greater durability is required, 120-gauge stretch wrap becomes the preferred option. At 30 microns thick, this film offers enhanced resistance to punctures and tearing, making it ideal for demanding conditions. This thicker film is often used for:
While 120-gauge film offers exceptional strength, it also comes with some trade-offs. Thicker films tend to be less flexible, making them harder to apply by hand. Additionally, they are more expensive compared to thinner options like 80-gauge film. However, the added durability justifies the cost for certain industries, such as manufacturing or logistics, where product safety is non-negotiable.
Pros and Cons of 120 Gauge Stretch Wrap:
Choosing between 80-gauge and 120-gauge stretch wrap depends on the specific needs of the packaging application. The stretch film mil to gauge chart helps businesses quickly identify the most suitable film by converting between these two units. For general-purpose use, 80-gauge film provides the perfect balance of strength, cost, and ease of application. However, for more demanding situations, 120-gauge film offers the durability needed to handle sharp or heavy loads.
Using the right gauge ensures not only the safety of the goods but also improves operational efficiency by minimizing waste and reducing the risk of product damage during transportation. Packaging professionals can benefit from online calculators to convert between microns and gauge, making it easier to align film thickness with load requirements.
By understanding the differences between these stretch film gauges and selecting the right one, businesses can optimize their packaging strategies, reduce costs, and ensure that products arrive safely and securely at their destination.
Selecting the right stretch film requires more than just knowing its thickness. Using micron to gauge stretch film measurements ensures precision when balancing flexibility, strength, and resistance for specific packaging needs. Several critical factors must be considered to guarantee optimal performance, including the load weight, environmental conditions, and the film’s stretchability and puncture resistance.
The weight of the load is one of the most important factors when selecting the appropriate stretch film thickness. Thicker films offer better durability and strength, while thinner films are suitable for lighter loads. Using micron to gauge conversion stretch film helps businesses match film thickness with load capacity, preventing over-packaging or under-packaging.
Matching the film’s thickness with the load weight helps minimize film usage while ensuring that products are securely wrapped. It also reduces the risk of product damage during shipping and lowers packaging costs by preventing overuse of material.
The conditions in which the stretch film is used and stored play a significant role in film selection. Factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to sunlight can affect the film’s performance.
Considering environmental factors helps businesses prevent packaging failures caused by extreme weather conditions or temperature shifts, reducing waste and product loss.
Choosing between flexibility and strength is another important consideration when working with micron to gauge stretch film. There is often a trade-off between the stretchability of the film and its ability to resist punctures or tearing.
Selecting the right film based on the required balance between stretchability and puncture resistance ensures packaging efficiency. Stretchable films reduce wrapping time and improve ease of use, while thicker, puncture-resistant films enhance durability and product protection.
Considering these factors ensures that businesses make informed decisions when choosing the right stretch wrap micron to gauge for their packaging needs. Evaluating load weight, environmental conditions, and the trade-offs between flexibility and strength guarantees optimal packaging performance. This strategic approach helps minimize waste, control costs, and protect goods throughout storage and transportation.
47 Gauge Hand Stretch Film
In micron to gauge stretch film calculations, the conversion ratio is straightforward: 1 gauge equals 0.254 microns. This means that for every gauge unit, the equivalent micron thickness is 0.254 microns. However, stretch films are usually measured in larger increments to match industry needs, such as 60-gauge, 80-gauge, or 120-gauge films. Understanding this conversion is important when switching between metric and imperial systems, especially for international businesses that work with both units. Using a micron to gauge stretch film calculator simplifies these conversions and ensures you select the appropriate thickness for your application.
Converting gauge to micron is simple using the following formula: Micron = Gauge × 0.254. For instance, 80 gauge multiplied by 0.254 gives 20.32 microns. This conversion ensures you can accurately measure the thickness of stretch films for various packaging needs. If you are using an online micron to gauge stretch film calculator, you can also perform reverse calculations to convert micron measurements back to gauge. Converting between these units helps maintain consistency, especially when working with international suppliers or customers who use metric systems for film specifications.
The gauge of stretch film refers to the thickness of the film, traditionally measured in units called gauge. This unit is commonly used in the U.S. packaging industry to determine how durable or flexible a film is. A higher gauge value indicates a thicker film, offering more strength and puncture resistance. For example, an 80-gauge stretch film is widely used for securing standard pallets, while thicker films, such as 120-gauge, are ideal for heavy-duty loads. Knowing how to convert between micron to gauge stretch film allows businesses to choose the appropriate thickness for their specific packaging requirements.
Gauge is a unit commonly used for measuring thickness in packaging films. To convert gauge to microns (µm), use the formula:
1 gauge = 0.254 microns.
For 60 gauge:
60×0.254=15.24microns.
So, 60 gauge equals approximately 15.24 microns.
Mil is another unit for thickness, primarily used in the U.S. One mil equals 25.4 microns or 100 gauge. To find the gauge for 2 mil:
2mil×100gauge/mil=200gauge.
A 2 mil stretch wrap corresponds to 200 gauge.
50 microns is equivalent to 0.05 millimeters (mm) or 0.00197 inches. In terms of stretch wrap, this is a mid-range thickness often used for heavy-duty applications.
A human hair is approximately 17 to 181 microns, depending on factors like ethnicity, age, and individual variation. On average, human hair measures around 70 microns.
1000 microns equals 1 millimeter (mm), which is a common benchmark for larger measurements.
20 microns is larger than 10 microns. To visualize, 20 microns is roughly the thickness of fine paper, whereas 10 microns is closer to the size of a bacterial cell.
2.5 microns is extremely thin, approximately 0.0025 millimeters (mm) or 0.000098 inches. This is close to the thickness of a thin plastic film.
The formula to convert gauge to microns is:
Microns = Gauge × 0.254.
Conversely, to convert microns to gauge:
Gauge = Microns ÷ 0.254. This ensures accurate conversion between the two units.

My name is James Thompson, and I’m the editor of this website dedicated to Stretch Film, Pallet Wrap, and Stretch Wrap products.
My passion for packaging began when I noticed the challenges companies face in securing their products efficiently for transportation and storage. This inspired me to delve deep into the world of stretch films and pallet wraps, exploring the latest technologies and best practices.
I aim to provide valuable insights, practical tips, and up-to-date industry trends to assist you in making informed decisions. Whether you’re a small business owner or part of a large corporation, my goal is to support you in optimizing your operations and ensuring your products reach their destination safely.
Thank you for visiting, and I look forward to accompanying you on your journey toward better packaging solutions.
Comments are closed