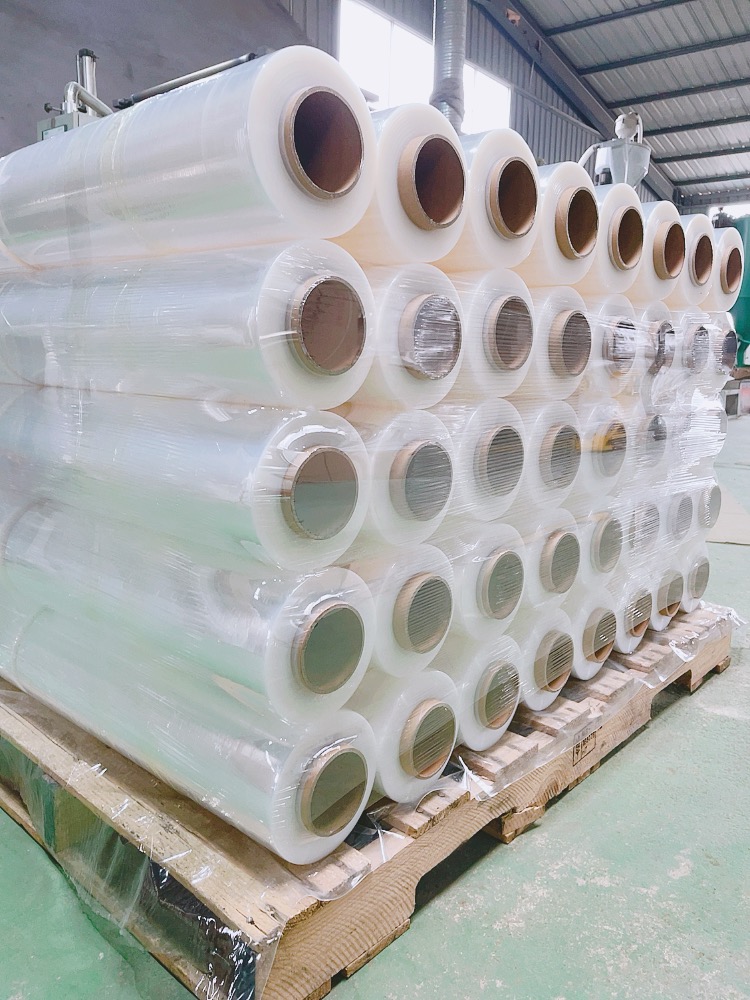
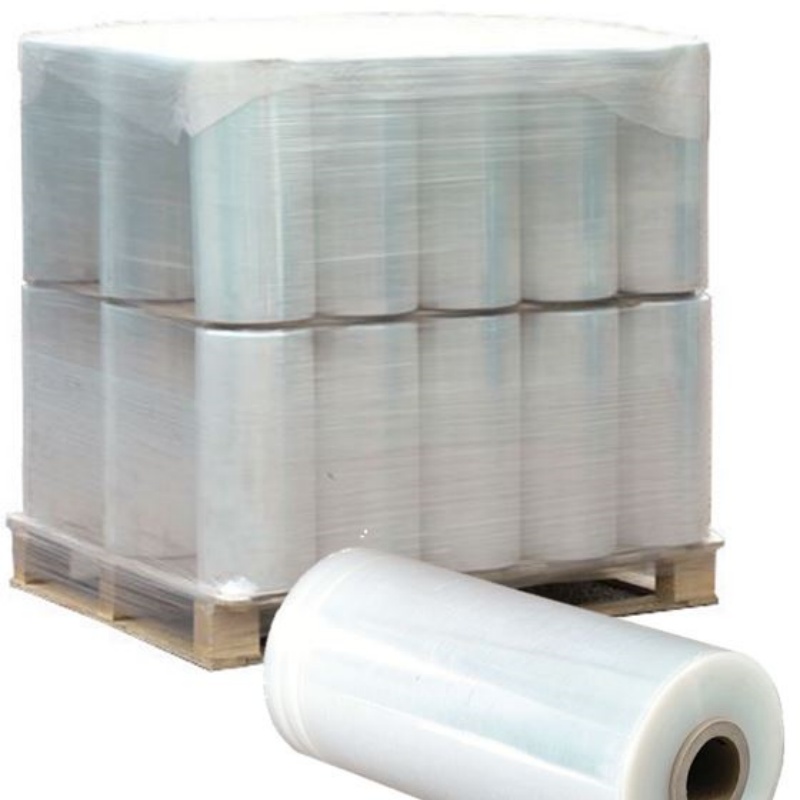
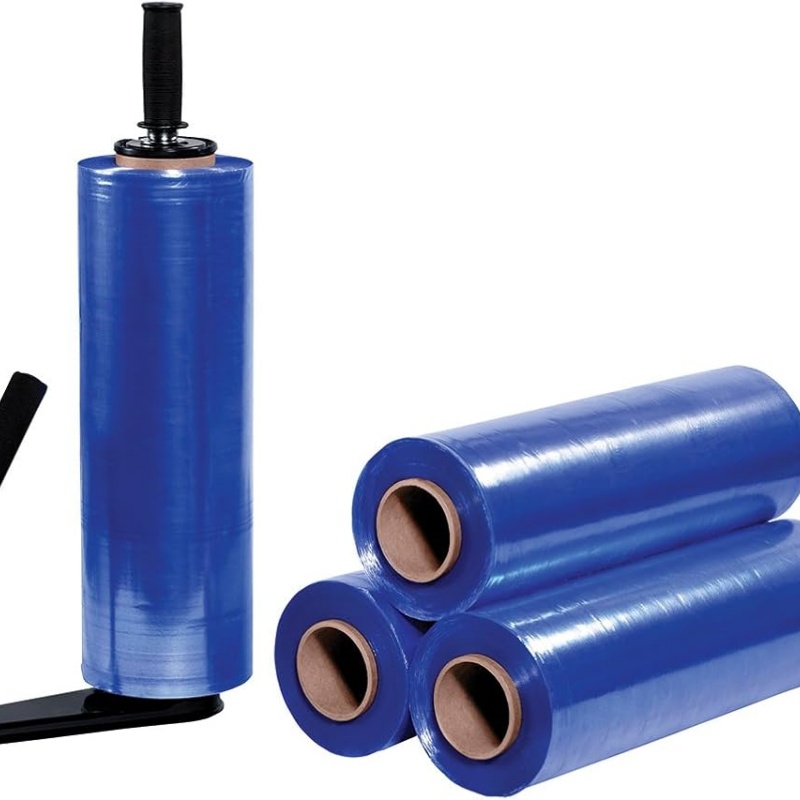
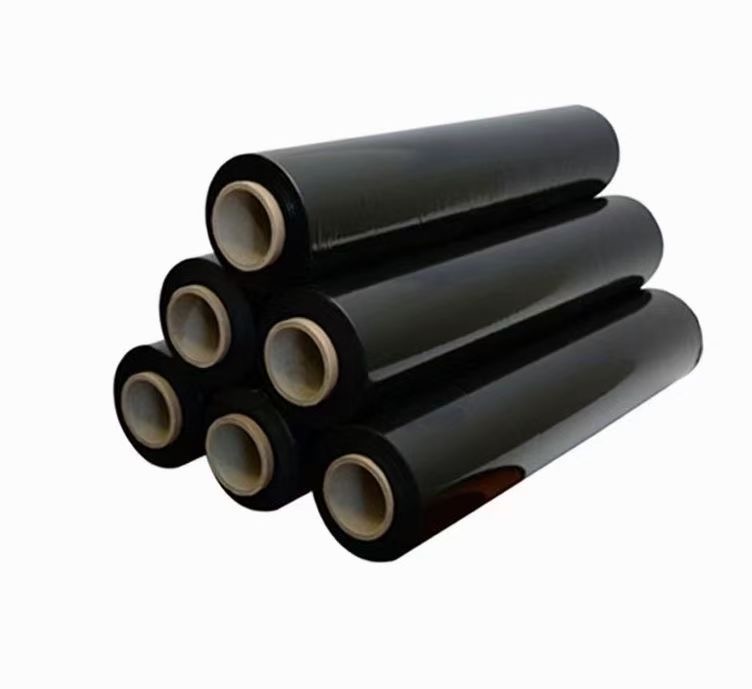
At PWP Stretch Film, we understand what matters most when choosing hand stretch film—strength, convenience, and sustainability. Our high performance hand stretch films are designed to deliver exceptional puncture resistance, high stretchability, and superior load stability, ensuring your products remain secure during storage and transportation.
✓ Military-Grade Protection
With 300% elongation at break and advanced puncture resistance technology, our film delivers 360° load stability – even for irregularly shaped items.
✓ Eco-Conscious Performance
Crafted with 100% virgin LLDPE resins from ExxonMobil/Dow/SABIC, we outperform recycled films with:
① 40% higher tensile strength
② Crystal-clear visibility for inventory tracking
③ Zero degradation during storage
✓ Engineered for Efficiency
Reduce material waste & labor costs with:
① Precision cling technology for single-layer wrapping
② Anti-slip texture for safer handling
③ Customizable widths (12″-24″) & thicknesses (15-30μm)
✓ Global Compliance, Local Agility
① ISO 9001 & ISO 14001 certified manufacturing
② 48-hour dispatch from our 12 global hubs
③ Custom color-coding solutions available (FDA-compliant pigments)